WhatsApp: +8619037303916
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +8619037303916
Email: [email protected]
As a specialist in crane hook production, we would like to introduce the types, manufacturing process, hook specifications and application scenarios.

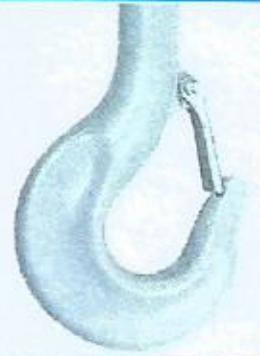
1.1 Crane hooks are divided into single hook and double hook according to the shape
The single hook is simple to manufacture and easy to use, but the force is not good, and it is mostly used in the workplace with a lifting capacity of less than 80 tons;
1.2 According to the manufacturing method, it is divided into forged hooks and laminated hooks
Large lifting weights often use symmetrical double hooks.
Laminated hooks are riveted from several cut and formed steel plates. When individual plates have cracks, the entire hook will not be damaged, and the safety is good.
However, the self-weight is large, and most of them are used on cranes with large lifting capacity or lifting steel buckets.
2.1 The purchased hook should have the manufacturer's certificate of conformity and other technical documents before it can be used.
2.2 The hook shall not have defects that affect the safe use performance;
Hook defects shall not be repaired by welding;
The surface of the hook should be smooth, and there should be no defects such as cracks, folds, sharp angles, burrs, peeling, and over-burning.
2.3 Two suitable positions can be selected at the shortest distance of the hook opening to print a mark that is not easy to wear and tear, and the distance of the mark can be measured as a basis for detecting whether the opening degree changes during use.
2.4 The hook material can be forged from the special material for the hook, and it is strictly forbidden to use the casting hook. The material of the plate hook is generally low alloy steel.
2.5 The technical conditions of self-made hooks should comply with FEM and GB standards.
2.6 The longitudinal axis of the hook piece of the plate hook must be located in the rolling direction of the steel plate, and the hook piece is not allowed to be spliced.
2.7 The hook piece of the plate hook should be riveted with countersunk rivets, and the high-stress bending part of the plate hook and the lifting point of the lifting object should not be connected by rivets.
2.8 Fully enclosed welding is not allowed between the plate hook laminations, only intermittent welding is allowed.
2.9 The hooks that have been subjected to the overload test should be discarded.
Kinocranes crane hooks are made of high-strength steel and undergo multiple processes, including forging, die forging, heat treatment, and machining. The surface of the hook is treated with sandblasting and pnting, making it corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing.
Hooks can be selected by referring to the following table.
|
Class |
Strength(kg/mm2) |
DIN |
AFNOR |
DIN15401 |
DIN15402 |
|
(M) |
40 |
AST41 |
XC18 |
 |
 |
|
P |
50 |
AST52 |
E36.4/20M5 |
||
|
(S) |
63 |
34CrMo4 |
34CD4 |
||
|
T |
80 |
34CrMo4 |
34CD4 |
||
|
V |
100 |
34CrNiMo6 |
35NCD6 |
|
Strength Class |
Drive group |
|||||||||
|
(M) |
- |
- |
M1 (1Dm) |
M2 (1cm) |
M3 (1Bm) |
M4 (1Am) |
M5 (2m) |
M6 (3m) |
M7 (4m) |
M8 (5m) |
|
P |
- |
M1 (1Dm) |
M2 (1cm) |
M3 (1Bm) |
M4 (1Am) |
M5 (2m) |
M6 (3m) |
M7 (4m) |
M8 (5m) |
- |
|
(S) |
M1 (1Dm) |
M2 (1cm) |
M3 (1Bm) |
M4 (1Am) |
M5 (2m) |
M6 (3m) |
M7 (4m) |
M8 (5m) |
- |
- |
|
T |
M2 (1cm) |
M3 (1Bm) |
M4 (1Am) |
M5 (2m) |
M6 (3m) |
M7 (4m) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
V |
M3 (1Bm) |
M4 (1Am) |
M5 (2m) |
M6 (3m) |
M7 (4m) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Hook# |
Lifting capacity |
|||||||||
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
2 |
1.6 |
1.25 |
1 |
0.8 |
0.63 |
|
1.6 |
8 |
6.3 |
4 |
4 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
2 |
1.6 |
1.25 |
1 |
|
2.5 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
5 |
4 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
2 |
1.6 |
|
4 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
5 |
4 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
|
5 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
5 |
4 |
3.2 |
|
6 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
5 |
4 |
|
8 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
5 |
|
10 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
6.3 |
|
12 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
8 |
|
16 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
10 |
|
20 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
12.5 |
|
25 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
16 |
|
32 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
20 |
|
40 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
25 |
|
50 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
32 |
|
63 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
40 |
|
80 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
50 |
|
100 |
500 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
63 |
|
125 |
500 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
80 |
|
|
160 |
500 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
100 |
||
|
200 |
500 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
125 |
|||
|
250 |
500 |
400 |
320 |
250 |
200 |
160 |
||||
|
Note: These hooks exist in 2 molds: RS: Forged in a mould RF: Free forged If customer requires a sample of proof test, a longer shank will be necessary. |
||||||||||
Crane hooks are widely used in ports, docks, factories, mines, construction sites, and other scenarios. They are suitable for lifting various heavy objects, such as steel plates, pipes, machinery and equipment, and building materials.
Kinocranes offer a wide range of crane hook specifications and can also provide customized services according to customer needs.
The hook should be scrapped when one of the following conditions occurs
4.1 Cracks appear
4.2 Dangerous section wear up to 10% of original size
4.3 The opening is 10% larger than the original size
4.4 The twisting deformation of the hook body exceeds 10°
4.5 The dangerous section of the hook or the neck of the hook is plastically deformed.
4.6 Hook thread corroded
4.7 When the hook bushing wear reaches 50% of the original size, the bushing should be replaced.
4.8 When the hook mandrel is worn up to 5% of the original size, the mandrel should be replaced.
Crane hooks are an essential component of crane machinery. Kinocranes hooks are made of high-strength steel and undergo multiple processes, making them corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing. They are widely used in various scenarios and can be customized according to customer needs. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
TO TOP